Iodine is a mineral that rarely gets the spotlight but is crucial for our overall health. This article takes you on a deep dive into the world of iodine. We will explore what iodine is, its vital role in our bodies, clear indications of iodine deficiency, and how you can ensure that you're getting enough iodine in your daily diet.
What is iodine?
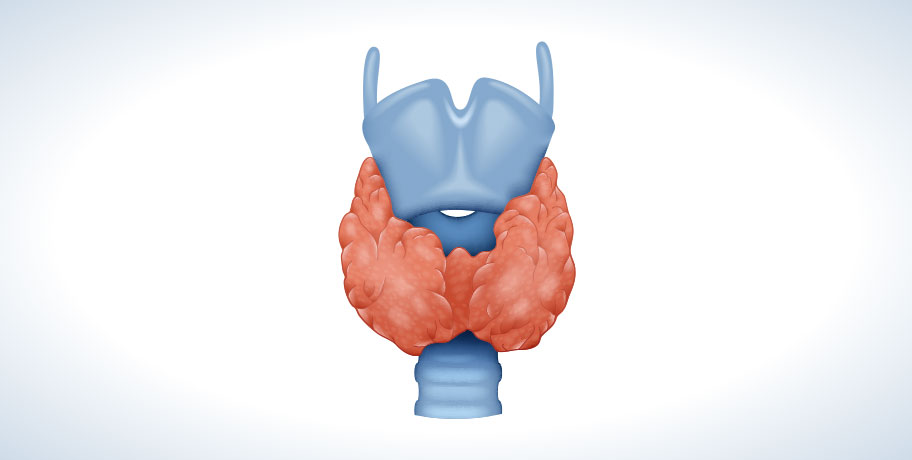
Iodine is an essential non-metallic element that is naturally found in certain foods and in the Earth's crust. Our bodies need iodine to produce thyroid hormones, which are essential for regulating metabolism. Thyroid hormones affect nearly every cell in the body and play a central role in the growth and development of our organs.
What is iodine good for?
Iodine has several important functions in the body:
- Thyroid health: Iodine is a key component of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4). These hormones regulate metabolism, energy levels, and body temperature. Iodine contributes to normal production of thyroid hormones and to normal thyroid function.
- Fetal development: During pregnancy, iodine is crucial for the development of the brain and nervous system in the fetus. Iodine deficiency in pregnant women can lead to serious complications for the child.
- Immune system: Iodine has also been shown to play a role in the function of the immune system.
- Iodine contributes to normal energy metabolism and to the normal function of the nervous system.
- Iodine helps maintain normal skin.
- Iodine contributes to normal cognitive function.
Can you overdose on iodine?
It is possible to overdose on iodine. The UL value (Upper Level or Tolerable Upper Intake Level) is a term used in nutritional science to indicate the highest daily amount of a nutrient that can be consumed without risking negative health effects. The UL value is established by expert panels that evaluate the available scientific research on nutrients and their potential risks. They take into account all known sources of the nutrient, including diet, supplements, and, in some cases, fortified foods. The UL value for iodine is 500 micrograms (µg) iodine per day from supplements according to CRN. Therefore, one should not take more than 500 micrograms of iodine per day from supplements.
How much iodine do you need per day?
The recommended daily intake (RDI) for iodine varies depending on age, gender, lifestyle, and health status. For adults, the RDI is:
Men and women's iodine needs: 150 µg
Pregnant women's iodine needs: 220 µg (higher to support fetal development)
Nursing women's iodine needs: 290 µg.
Does iodine testing on the skin work?
Skin iodine testing has very low reliability, and it is not something we recommend.
Is iodine deficiency common among pregnant women?
Pregnant women are at risk for iodine deficiency and are in greatest need of it.
Summary on iodine
Iodine is an essential mineral that plays a critical role in our thyroid health and many other bodily functions. Iodine deficiency can lead to serious health problems, so it's important to ensure that you're getting enough iodine through your diet or supplements if needed.
Sources & References
Food Agency: https://www.livsmedelsverket.se
Delange F, Bürgi H. Bull World Health Organ. 1989 PMCID: PMC2491245.
